The price of a financial asset, such as a stock, currency pair, or commodity, is critical to trading because the price change determines profit or loss.
Price action trading is to work on the bare basics of trading rather than using chart pattern recognition or technical indicators deduced from price moves and having a natural delay. You get all the data you need to trade trends, breakouts, and swings by studying price movement over a particular timeframe.
Want to learn more about price action and price action trading? Then keep reading because we’ll go over everything there is to know about it.
What does Price Action Mean?
Price action is the trend or character of how the price of a security or asset performs, typically in the brief term. It forms the basis for all technical analyses of a commodity, stock, or asset chart. It is straightforward to analyze when price action is plotted graphically over time.
It can be analyzed using a variety of charting tools and chart configurations. The most common are the Japanese candlestick chart, the line chart, and the bar chart. These depict price action in various ways, and traders use them to recognize and analyze market trends.
It’s important to note that each of these chart settings has its own set of advantages, and which one to use for price action analysis is a matter of individual preference.
What is Price Action Trading?
Price Action Trading is the process of creating all trading decisions based on a simplified or “naked” price chart. This means no slowing indicators other than perhaps a couple of moving averages to assist in identifying vibrant support and resistance areas and trends.
Price action trading ignores the primary factors that impact a market’s movement and instead focuses on its price graph or its price movement over time.
Price action is a type of technical analysis. But what distinguishes it from most other types of analysis is that its primary focus is the relationship between a market’s current price and its past or recent prices.
How to do Process Trading?
Most skilled price action traders maintain several options for recognizing trading strategies, entry and exit levels, stop-losses, and other related findings.
Using only one strategy on one or more stocks may not provide enough trading opportunities. The majority of situations involve a two-step procedure:
- Recognizing a scenario: For example, a stock price entering a bull/bear process, channel range, breakthrough, and so on.
- Trying to identify trading opportunities within the situation: For example, if a stock is on a bull run, is it likely to either overshoot or retreat? This purely subjective decision can differ from one trader to the next, even when presented with the same circumstance.
What are Price Action Trading Strategies?
A trading strategy must include three components: why, how, and what.
The ‘why’ is the leading cause you are considering trading a specific market. This is where price action trends come into play. The ‘how’ is the dynamics of your trade. In essence, it is the mode in which you will trade. The ‘what’ is the result of the trade. What do you wish to get from it?

Price action patterns, also known as price action triggers or signals, are essential in price action trading because they offer a powerful trader hint as to what price could do next. Here are some price action trading strategies.
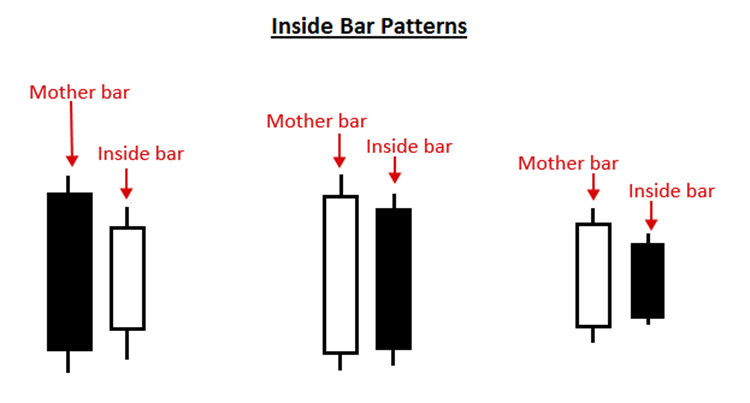
1. The Inside-Bar Pattern
An inside bar pattern comprises the inside bar and the previous bar, typically known as the “mother bar.”
In trendiest markets, this price action strategy is standard as a breakout pattern, but it can also be decided to trade as a reversal signal if it creates at a key chart level.
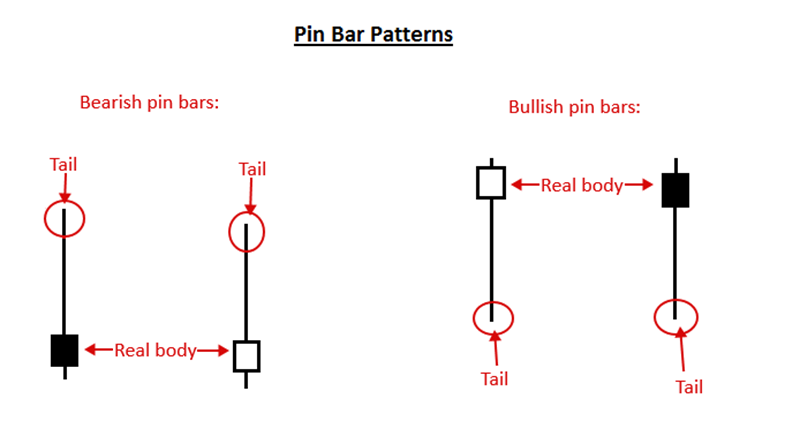
2. The Pin Bar Pattern
A pin bar pattern is composed of only one candlestick, indicating price rejection and a market inversion. The pin bar signal works well in a trending or range-bound market and can also work on trading counter-trend from a critical support or resistance level.
The pin bar suggests that the price may be moving in the opposite direction of the tail, as the pin bar’s tail indicates price rejection and a reversal.
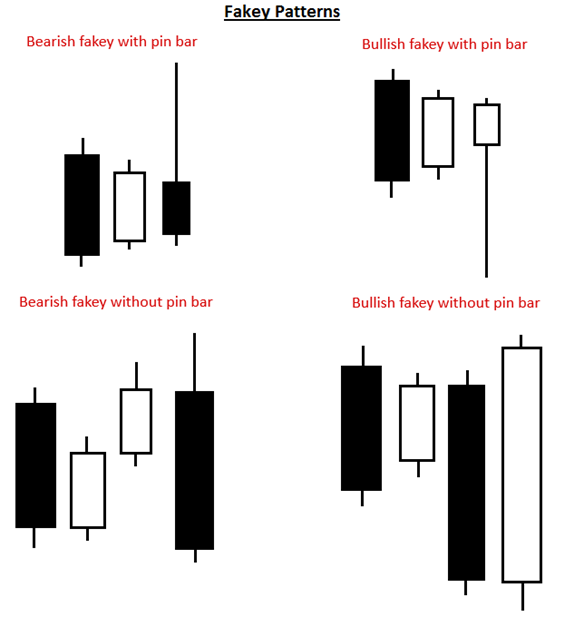
3. The Fakey Pattern
A fakey pattern is a falsified breakout from an inside bar pattern. In other words, a fakey occurs when an inside bar pattern starts to break out momentarily but then overturns and closes back within the spectrum of the mother bar or inside the bar.
It’s called a “fakey” because it deceives you. The market appears to be splitting one way but reverses and causes a price action in the opposite direction.
Conclusion
Price action studies the characteristics of a security, index, commodity, or currency to forecast what it will do in the future.
Price action trading strategies can be as simple or complex as you want them to be. Whatever strategy or system you try to trade with, understanding price action trading will make you a better trader.
While we have discussed a few common market patterns, examine your previous trades to see if you can identify tradeable patterns. The important thing for you is to get to the point where you can locate one or two strategies.


0 Comments